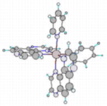
The "Chiral Building Blocks" synthesis strategy requires the synthesis and optical resolution of precursor complexes. The advantage of this method consists in obtaining a precursor which can then be used for the synthesis of many different complexes so that resolution methods do not have to be accommodated to each target complexes. The precursor complexes chosen in this study are [Ru(L)2(pyridine)2] (on the figure L = TAP).
The results are developped in the following sections presented on this page as thumbnails. Clicking on the different schemes and figures will lead you to full size pictures and to more comments and references. You can come back to this results page by using the links or browsing the back button.Return to main page
I. Synthesis of [Ru(L)2(pyridine)2]2+The synthesis of the 2 precursors was performed in 2 steps as described in the litterature. Both precursors were caracterised by Electro-Spray Mass Spectrometry and 1H NMR in one and two dimensions.
click to get full size picture and more information
II. Resolution of [Ru(L)2(pyridine)2]2+The optical resolution of the precursors [Ru(phen)2(pyridine)2]2+ was achieved by diastereoisomeric crystallisation as described in the litterature. The enantiomeric excess obtained with [Ru(phen)2(pyridine)2]2+ has been determined by the determination of the specific optical rotation.
Application of this separation method to the TAP analogue did not succeed however, pointing out the difficulty of generalisation of optical resolution methods. Two other resolving agents were used with different methods but until now, no resolution has been achieved on this precursor.
click to get full size picture and more information
III. Photophysical Properties of [Ru(TAP)2(pyridine)2]2+ : Importance of PhotoracemisationThe photophysical properties of the racmic mixture of [Ru(TAP)2(pyridine)2]2+ were investigated in order to evidence the main deactivation pathway and thereby reasoning on the origin of photoracemisation of this class of compounds.
click to get full size picture and more information
Return
to main page to switch to the conclusion part of this contribution