![]()
EXPERIMENTAL
![]()
System
The experiments were carried out in a low-temperature photochemical reactor made of glass (See Figure 1). The selected temperature was obtained by the control of the flow of liquid air evaporated from a liquid air reservoir. The temperature was achieved by a resistively heated electrical resistance immersed in liquid air. The temperature regulation consisted of controlling the frequency of a pulsed potential applied to the resistance.
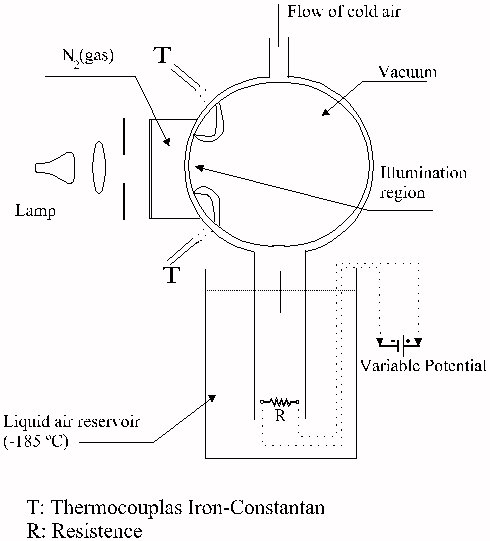
Figure 1. Squematic diagram of the experimental set up
Temperature range: 120-250 K (± 1 K)
Excitation sources: High pressure Mercury lamp (200 W), Conventional Halogen lamp (50 W, divergence 10º)
Product analysis: UV, IR spectroscopy, Mass spectrometry
Synthesis:
ClF (g) + HNO3 (-60ºC, dehydrated) ¾® ClONO2 + FH
Vacuum system: Conventional grass free.
Procedure
The water and chlorine nitrate were deposited on the glass surface directly from the gas phase.
Sequence of the experiments
1) Deposition of water
2) Deposition of Chlorine Nitrate
3) t (minutes) under dark reaction conditions. Then: analysis of gaseous products.
4) t (minutes) under illumination conditions. Then: analysis of gaseous products.
![]()
INTRODUCTION EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS DISCUSSION ATMOSPHERIC IMPLICATIONS REFERENCES