RESULTS
 Figure 2.
Gaseous products found in the photolysis of ClONO2 adsorbed on ice.
Figure 2.
Gaseous products found in the photolysis of ClONO2 adsorbed on ice.
T = 200 K Excitation source: High pressure Hg lamp.
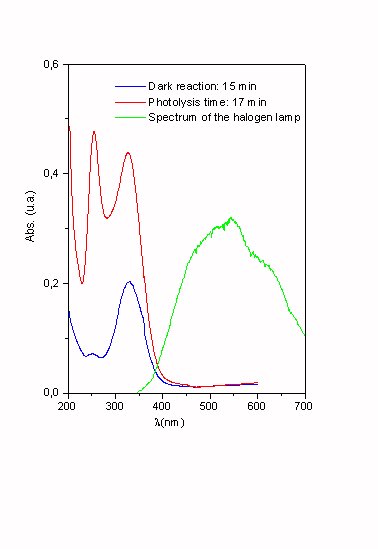
Figure 3. Gaseous products found in the photolysis of ClONO2 adsorbed on ice as a function of the photolysis time.
T = 200 K Excitation source: Halogen lamp.
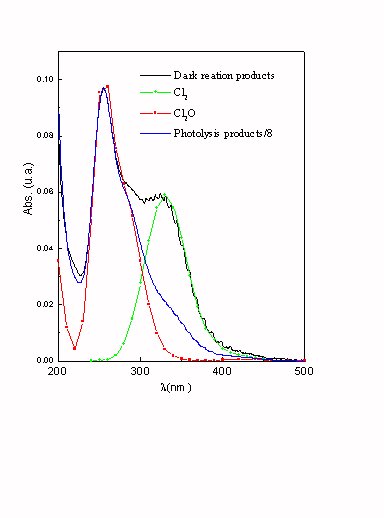
Figure 4. Comparison between UV spectra of photochemical gaseous products and bibliography3.
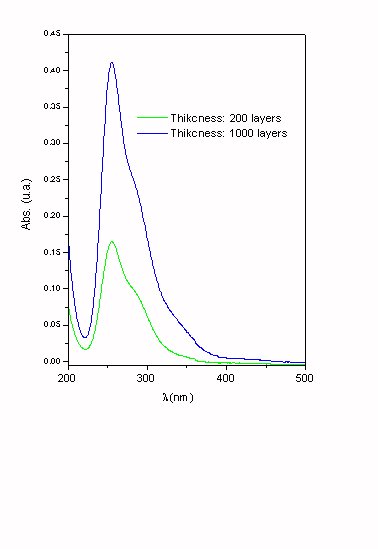
Figure 5. Photochemical gaseous products obtained at different thickness of ClONO2 adsorbed on ice.
T = 200 K. Photolysis time: 10 min. (Hg lamp). The thickness was estimated assuming a ClONO2 molecular radio of 3.59 Å calculated using the program Gaussian94 (Base 6-31g*).
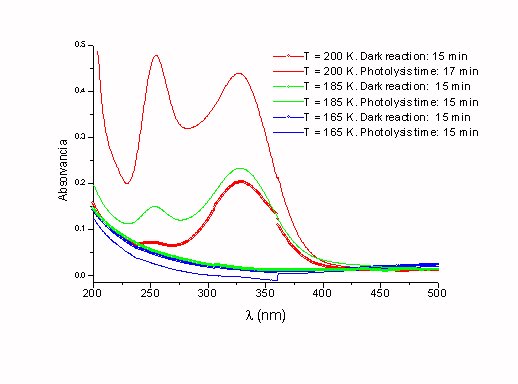
Figure 6. Photochemical gaseous products obtained at various temperatures.
Excitation source: Halogen lamp.
![]()
Table 1. Percentage of ClONO2 decomposed under illumination calculated as:
2 x (mole of Cl2 + mole of Cl2O). Excitation source: Hg lamp
Mole of ClONO2 x 1005 |
Photolysis time (min.) |
Temp. (K) |
Mole of Cl2 x 1006 |
Mole of Cl2O x 1006 |
Conversion (%) |
7,5 |
Only dark reaction: 25 |
199 |
0.039 |
0.66 |
£ 2 |
7.5 |
25 |
199 |
7.6 |
5.3 |
³ 35 |
2.0 |
10 |
200 |
3.6 |
2.8 |
³ 65 |
0.45 |
10 |
200 |
0.5 |
1.1 |
³ 70 |
5.0* |
40 |
185 |
10.9 |
0.97 |
£ 40 |
* Excitation source: Halogen lamp
![]()
INTRODUCTION EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS DISCUSSION ATMOSPHERIC IMPLICATIONS REFERENCES